NEWSLETTER
Selenium supply in Germany
Under-supplied across the board – BfArM also knows
Whether Immune System, Fertility, Detoxification or Thyroid: Selenium is a “big player”. Unfortunately, the supply in this country leaves a lot to be desired.
Our tip: Supplement

Selenium – good protection for our body
Selenium – effect and daily requirement
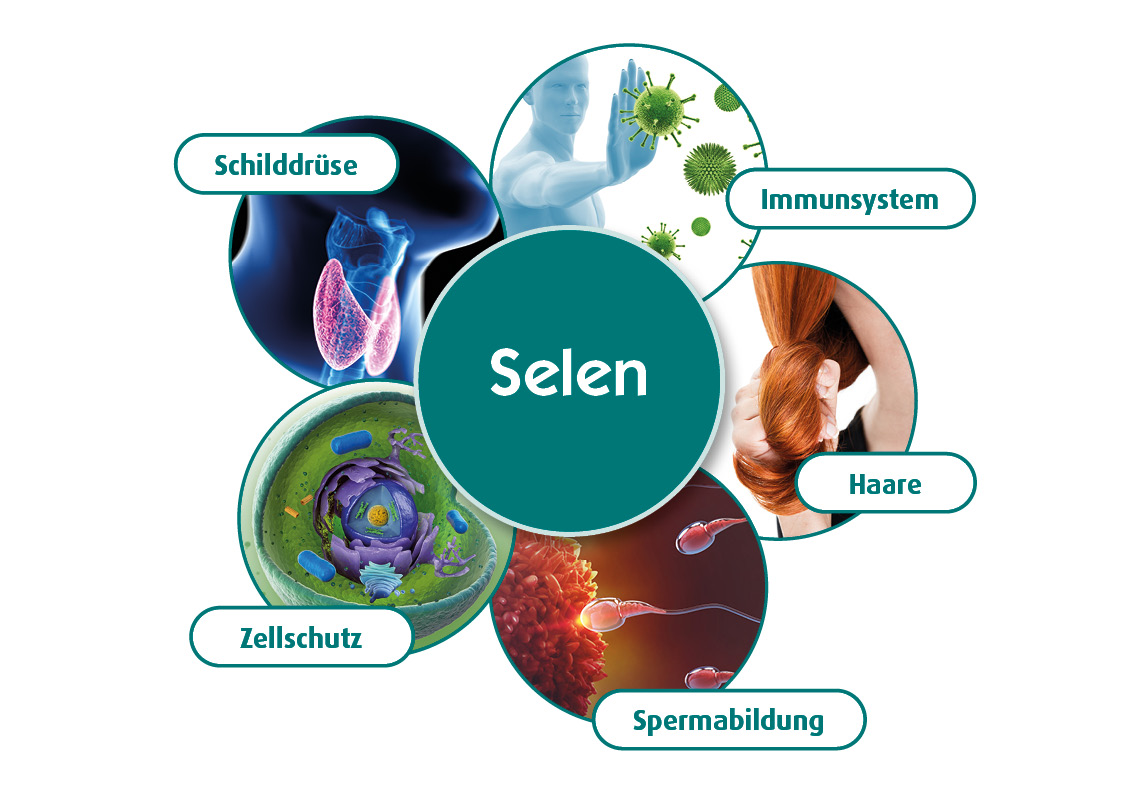
Selenium is a micronutrient with numerous effects: It has an antioxidant effect, is involved in the regeneration of Q10 as well as glutathione, neutralizes hydrogen peroxide produced in the thyroid gland and is an essential micronutrient for a powerful Immune System. Deiodases, which convert the thyroid hormone T4 into the actual active form T3, are also dependent on an adequate supply of Selenium. Reason enough to take a closer look at this trace element.
Selenoproteins fulfill a wide variety of functions in the body. Glutathione peroxidase and the thioredoxin reductase family, for example, are involved in the body’s cellular antioxidant defense system, while a selenium-containing transport protein has a protective effect on the endothelium. A lack of Selenium could therefore potentially have an impact on a wide range of diseases such as cancer, intestinal inflammation, diabetes mellitus, depression and much more. Unfortunately, our soils in this country are low in selenium. This means that food is also low in selenium and the requirement can hardly be covered by a normal diet – and on top of that, the current standard value for the selenium blood level no longer corresponds to the current state of science.
Because when it comes to prevention or systematic therapy, it is set far too low.
So much for the theory. What does it look like in practice? Let’s take a look at the literature. BfArM published the following on Selenium intake in 2021:
“There are currently no current data available on selenium intake in Germany via the diet. Selenium intake was not determined in the National Nutrition Survey II8 ; the Federal Food Code does not contain any information on selenium content.”
You might think: What is not known will fit. Or would it not?
It continues: “Oster et al. have estimated a selenium intake of 47 µg/day (men) and 38 µg/day (women), corresponding to 0.67 µg/kg body weight [1], for the old federal states on the basis of measured selenium levels in food and average food consumption.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) warns that these data should be interpreted with caution. Nevertheless, the BfArM also concludes: “Compared to the D-A-CH and EFSA estimates for adequate intake, the estimated median selenium intake for adults in various EU countries is below the intake recommendations.”
Prevention and therapy
Selenium – A vital trace element
The estimates are also consistent with the results of another survey that collected blood level measurements: “As part of a study carried out between 1987 and 1989, the composite study Nutrition Survey and Risk Factor Analysis (“VERA Study”), a median serum selenium concentration of 82 µg/l for men and 83 µg/l for women was determined for the old federal states. Measured against the reference range for adults of 74- 139 µg/l, the serum selenium concentration is in the middle to lower range.”
However, ideal preventive effects require blood level concentrations of 130 to 150 ug/L, as Selenium-dependent enzymes only reach their maximum activity above 120 ug/L! Functional medicine focuses on providing the body with optimal conditions for prevention. Studies have also come to the conclusion that cardiovascular diseases such as heart failure, myocardial infarction (click here ) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (click here) correlate with lower selenium levels.
Not a good idea: Brazil nuts
Finland reacted to the extremely low selenium intake by introducing the use of fertilizers containing sodium selenate nationwide in 1984. This actually raised the average plasma Selenium concentration in the population from 0.89 µmol/L to an average of 1.40 µmol/L and thus into the optimal range.
In this country, however, individual initiative is still required. Time and again you read the tip to “naturally” improve your selenium supply with Brazil nuts, as they are particularly rich in selenium. However, Brazil nuts contain a lot of radium. The Federal Office for Radiation Protection (click here) points out that just two Brazil nuts a day increase the natural radioactive dose from food by half and that it is possible to correct this without any additional radiation exposure by taking food supplements.
We agree with this tip: Have your selenium blood level determined and supplement. The EFSA names 255 ug Selenium per day as the Tolerable Upper Limit (UL).
Source:
Selenium and Selenoproteins in Health
[1] The daily dietary selenium intake of West German adults









