NEWSLETTER
TicToc weight loss trend Ozempic
Effect via gut microbiome?!
Disturbed intestinal flora
Dysbiosis – an imbalance in the intestinal flora
Dysbiosis is now associated with numerous diseases. These range from irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory diseases to cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune diseases, neurological diseases (depression, Parkinson’s, autism) or allergies and asthma. Short-chain fatty acids play a key role in this, for example by modulating the gut-brain axis or the gut-associated Immune System. They serve as signaling molecules of the gut-brain axis. In order for these to be formed in sufficient quantities, a high diversity of dietary fibres and colonization with bifidobacteria and butyrate-forming strains such as Faecalibacterium prausnitzii are essential. F. prausnitzii is also considered a decisive germ for the assessment of intestinal flora health. In Healthy adults, it is one of the most abundant species in the intestinal flora with 5 to 10 %.
However, a reduced number can be observed not only in diabetics and obese people. Michalik et al ( PubMed: Alteration of indicator gut microbiota in patients with chronic sinusitis ) recently published their findings that patients with chronic sinusitis also have a reduced number of Bifidobacterium spp and F. prausnitzii. In addition to a reduction in bifidobacteria, Akkermansia muciniphila was also significantly reduced in the majority of them. These are involved in the nutrition and regeneration of intestinal epithelial cells and the mucus and have anti-inflammatory properties.
The research results support the hypothesis that a disturbed microflora in the sinuses could be linked to intestinal dysbiosis. The treatment of chronic sinusitis is sometimes difficult despite prolonged antibiotic therapy. Those affected could potentially benefit from the intake of pre- and probiotic therapy to support the intestinal microbiome and mucosal immunity. In particular, non-pathogenic intestinal bacteria such as Enterococcus spp appear to stimulate plasma cells and thus induce the formation of secretory IgA on all mucosal surfaces. They prevent the attachment of pathogenic bacteria and viruses.
-
 Themed world Gut HealthOrthoDoc
Themed world Gut HealthOrthoDocMucosa
29,95 €83,19 €/kgFood supplement with resistant starch, L-glutamine, biotin, niacin, riboflavin, lactic acid & bifido cultures
Available immediately -
 aminoplusMonosubstances
aminoplusMonosubstancesaminoplus® Glutamine pure
29,95 €72,34 €/kgFood supplement with L-glutamine
Available immediately -
 OrthoDocExtracts & Probiotics
OrthoDocExtracts & ProbioticsIntestinal Cleanse
39,90 €39,90 €/kgFood supplement with lactic acid bacteria
Available immediately

The intestinal presence of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii also appears to be beneficial in diabetes. A study(PubMed: Faecalibacterium prausnitzii phylotypes in type two diabetic, obese, and lean control subjects) found that F. prausnitzii was significantly reduced in diabetic and obese individuals compared to lean control subjects. The mechanisms of gut flora in the treatment of type 2 diabetes are not yet fully understood. Moderate butyrate levels can prevent insulin resistance triggered by a high-fat diet through epigenetic effects. They also increase mitochondrial beta-oxidation and thus improve glucose sensitivity and influence obesity. Further effects on insulin sensitivity are being discussed by influencing bile acid production or endotoxin inflammation.
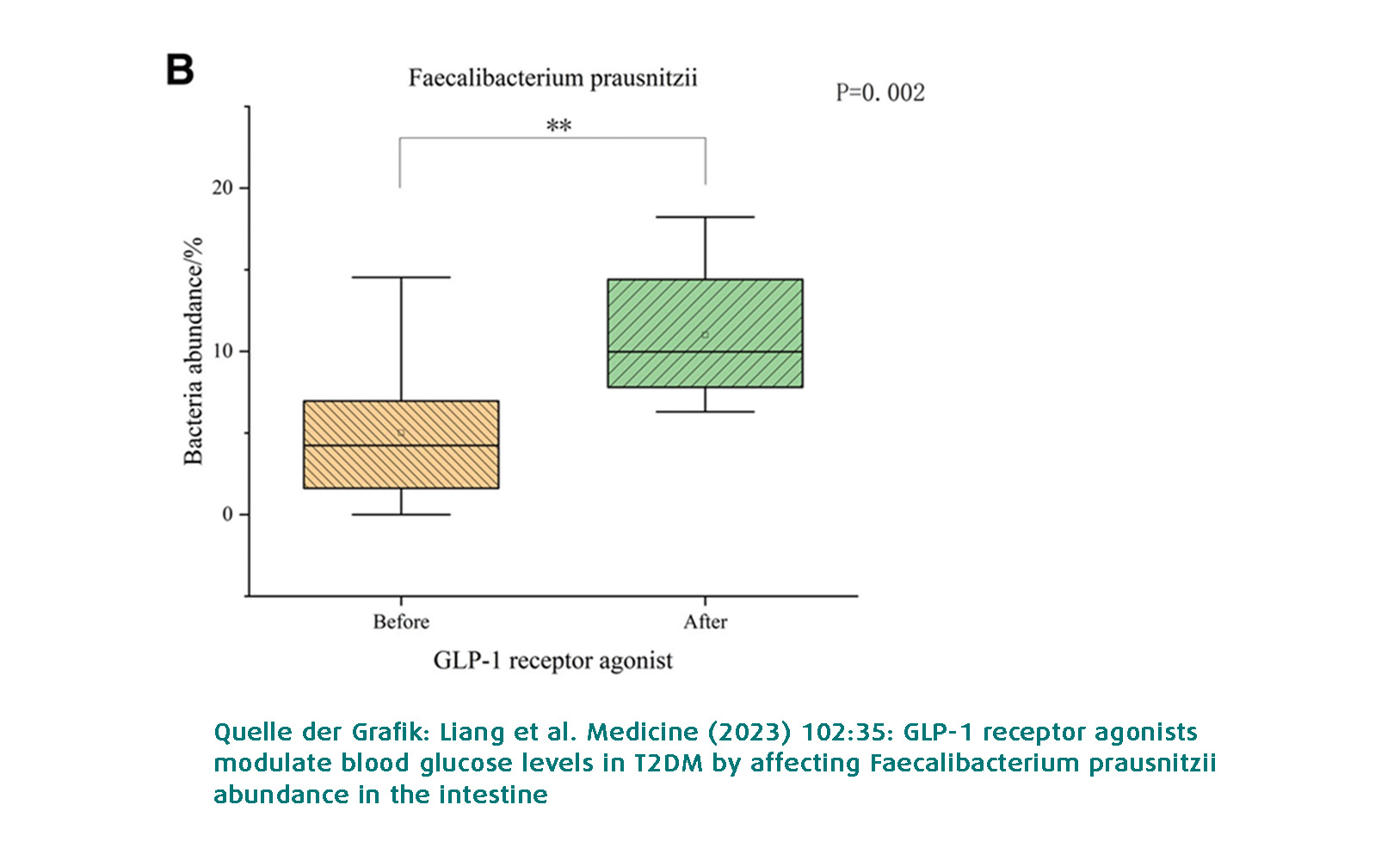
Interestingly, a team led by Liang(PubMed: GLP-1 receptor agonists modulate blood glucose levels in T2DM by affecting Faecalibacterium prausnitzii abundance in the intestine) has now discovered that influencing F. prausnitzii colonization could actually be one of the pathways behind the effect of so-called glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists. Semaglutide (Ozempic) is probably the best-known representative of GLP agonists and, along with other active ingredients, has a firm place in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Just one week after the use of a glucagon-like peptide agonist, the proportion of F. prausnitzii increased significantly and correlated negatively with fasting glucose.
GLP receptor agonists have a positive effect on the feeling of satiety and also support weight loss. Semaglutide is on everyone’s lips as a “slimming injection”, not least due to a Tic-Toc trend, and has led to persistent supply bottlenecks due to off-label use. Demand has risen to such an extent that the BfArM(BfArM: Falsification of the drug Ozempic®) has recently even had to warn against counterfeiting the drug Ozempic©.
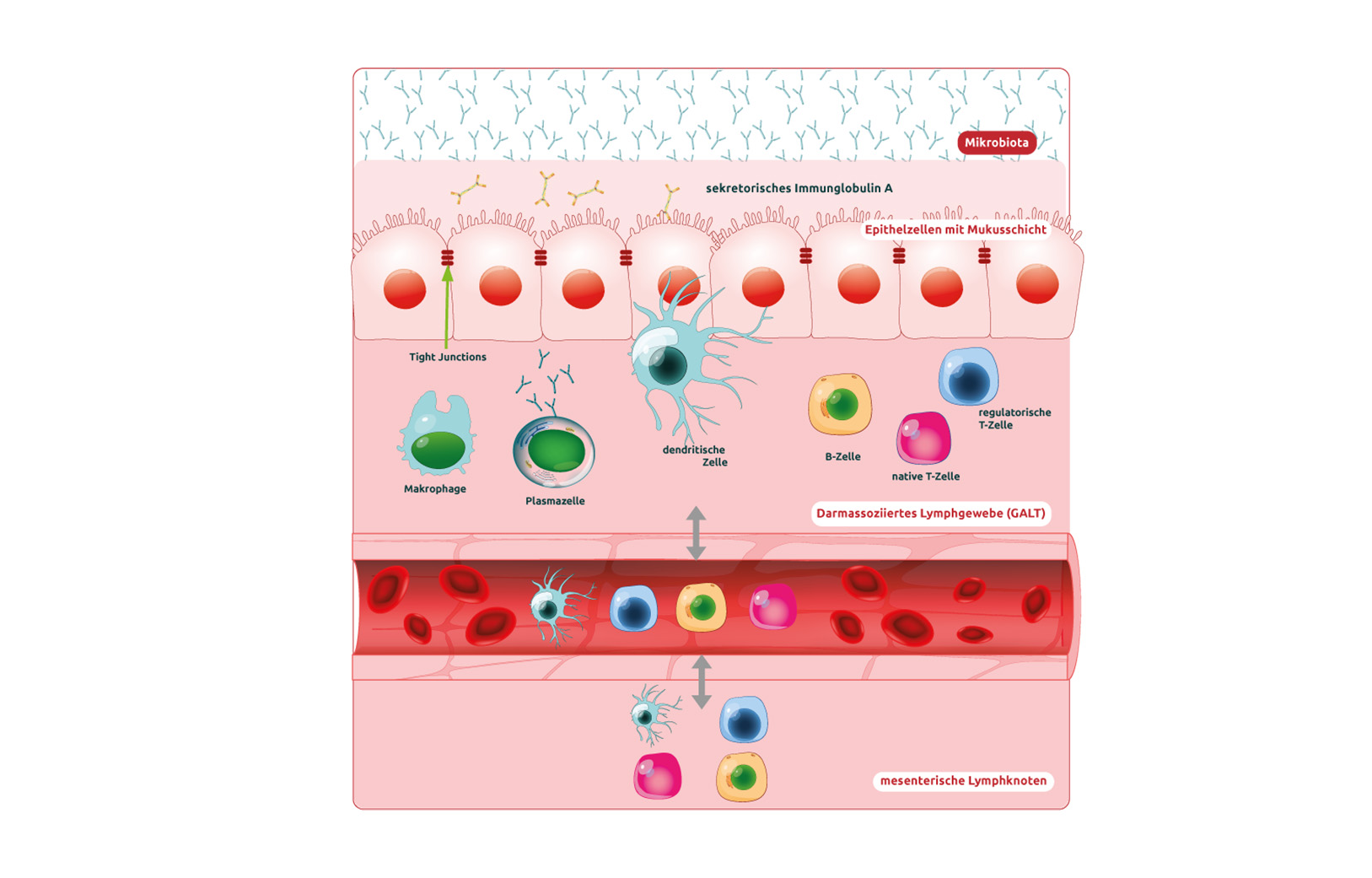

In chronic rhinosinusitis, the mucous membranes of the nasal cavities and sinuses swell and cilia function is impaired. Due to their conditions (temperature, humidity, protected cavity), the paranasal sinuses provide an ideal microbial habitat for both beneficial and pathogenic germs. Key elements of the mucosal Immune System are B and T lymphocytes, natural killer cells and macrophages. The immunological training of the lymphocytes takes place in the so-called Peyer’s plaques (= part of the gut-associated lymphoid tissue, GALT). The immune cells are activated by cytokines in Contact with the physiological microbiota and eventually plasma cells are formed. They spread throughout the body and produce sIgA. It remains exciting to see what other areas of application for pre- and probiotics current research will discover.