NEWSLETTER
Prevention: Vitamin D
Should I take a daily vitamin D supplement?
A new meta-analysis impressively shows that daily supplementation with vitamin D reduces the risk of cancer – but bolus administration does not…

Only daily vitamin D scores
Cancer mortality drops by 12
Prevention is better than cure! This is shown not least by a recently published meta-analysis on the subject of vitamin D. It included a total of 9,4068 patients and came to the conclusion that taking vitamin D could reduce cancer mortality by up to 12 percent! However, this was only the case with daily intake, as a bolus regime did not reduce mortality. Patients over the age of 70 and patients who started taking vitamin D before a cancer diagnosis benefited the most.
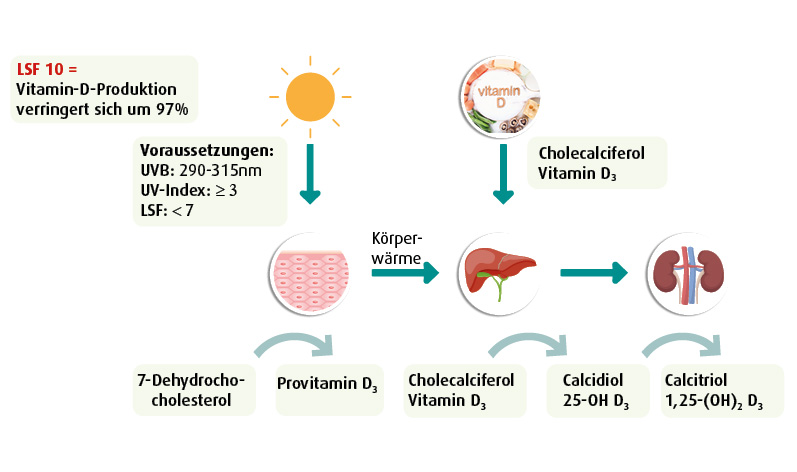
In fact, the vitamin D requirement cannot be met through diet. Instead, endogenous synthesis via the skin or exogenous intake is necessary. However, anyone who wants to make up for a vitamin D deficit in the summer months with an extra portion of sun is not yet aware of the consensus recommendation of the Federal Office for Radiation Protection on UV radiation and vitamin D. It strongly advises against strong UV radiation for the purpose of vitamin D formation or self-therapy of a vitamin D deficiency.

Background knowledge on vitamin D
Half-life only 24 hours
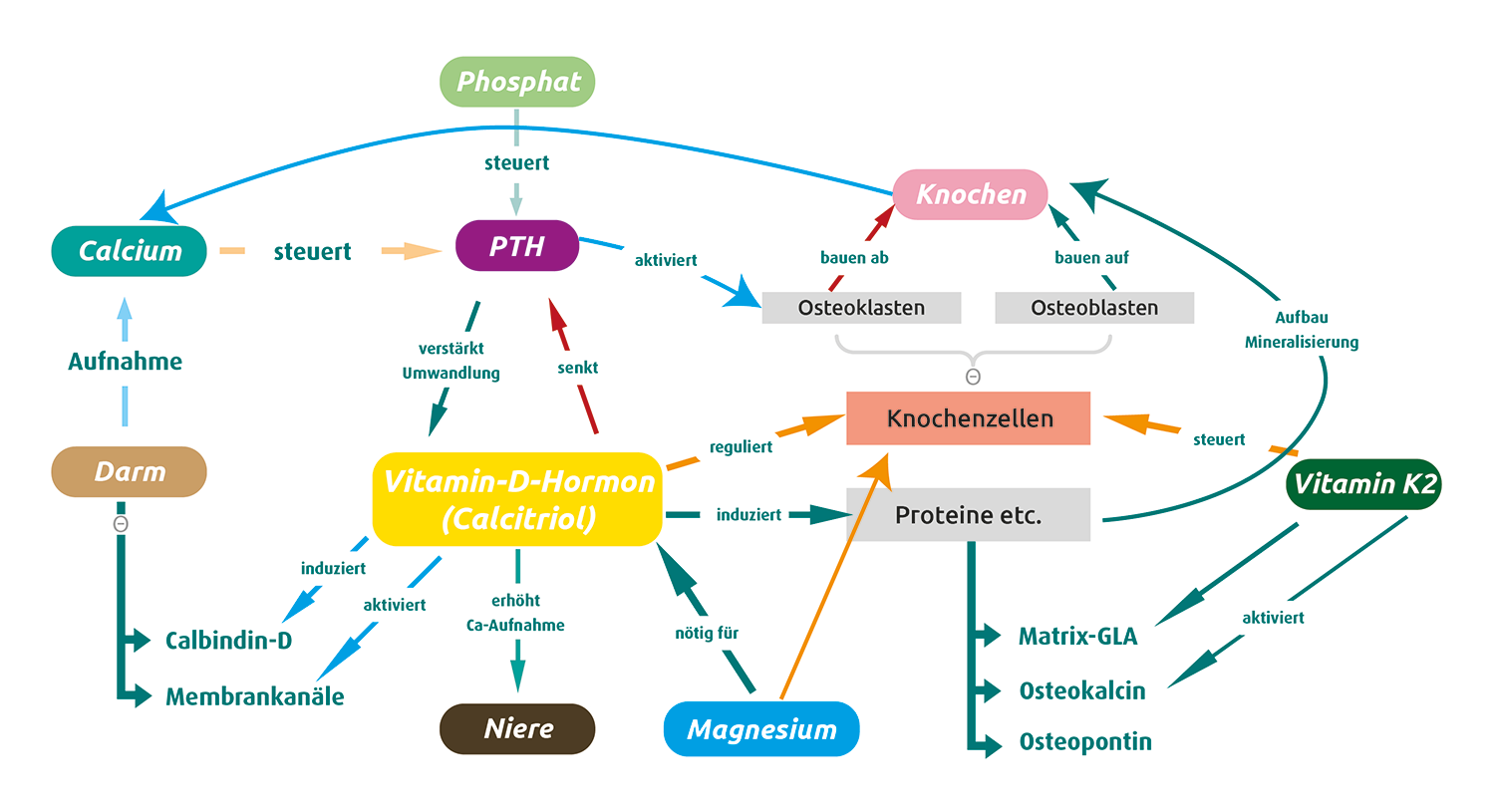
The endogenous synthesis of vitamin D in the body begins with the exposure of the skin to UVB radiation (280 – 315 nm, maximum effect approx. 295 nm). This radiation converts 7-dehydrocholesterol, a precursor molecule in the skin, into vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol). It is then transported to the liver, where it is hydroxylated to 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (=25(OH)D3, calcidiol). From the liver, calcidiol reaches the kidneys, where it is further hydroxylated to form calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D in the body.
If patients want to know their vitamin D3 status, the laboratory determines the 25(OH)D3 level. Although the half-life of calcidiol (=25(OH)D3) is 3 weeks, that of vitamin D3 (=cholecalciferol) is only around 24 hours! Therefore, even with good values, a daily supply of vitamin D3 is still necessary – whether in the summer months via endogenous synthesis through the skin or exogenously. This is the only way to ensure a good supply at the cellular level.
Incidentally, both the enzymes involved in the synthesis of vitamin D and vitamin D transport molecules are Magnesium-dependent. A Magnesium deficiency therefore disrupts vitamin D metabolism in all areas.
Source: Micronutrient therapy, Edmund & Nathalie Schmidt,
Don’t forget UV protection
Skin cancer on the rise
The background to the warning is the fact that skin cancer has been on the rise for decades. According to the current S3 guideline “Prevention of skin cancer”, the probability of squamous cell carcinoma correlates with the cumulative UV dose that a person absorbs in the course of their life. This also increases the risk of basal cell carcinoma, whereby intermittent UV exposure and sunburn also appear to be significant. This also applies to malignant melanoma.
Especially in the summer months, avoid the intense midday sun and protect the skin with clothing and suitable sun protection. This also offers cosmetic benefits. After all, UV-A rays are responsible for a large part of visible skin ageing. So vanity does not exclude Health. Unfortunately, sun protection measures prevent vitamin D synthesis, so in certain cases supplementation may also be indicated in the summer months.