Micronutrient therapy
Understanding and combating movement restrictions
As temperatures rise, the desire to exercise increases. But pain-free movement is not a matter of course: in the 50 to 54 age group alone, 15-16% of Germans already suffer from radiological signs of osteoarthritis of the knee, as the current S2k guideline on osteoarthritis of the knee states(AWMF-online: Osteoarthritis of the knee). Between the ages of 70 and 74, as many as 36 to 40 percent show visible signs of knee osteoarthritis. “Clinically, the disease presents with inflammatory and non-inflammatory phases. Only some of the patients with radiological changes have functional disorders and pain,” it continues. Patients who present to the practice or surgery with pain often have a considerable amount of suffering. This is because movement is an essential pillar of quality of life and, if restricted, leads to a vicious circle of lack of movement, increasingly poor joint care and ever-increasing progression of osteoarthritis. Reason enough to take a closer look at the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis and the opportunities offered by micronutrient therapy.
For information
For information:
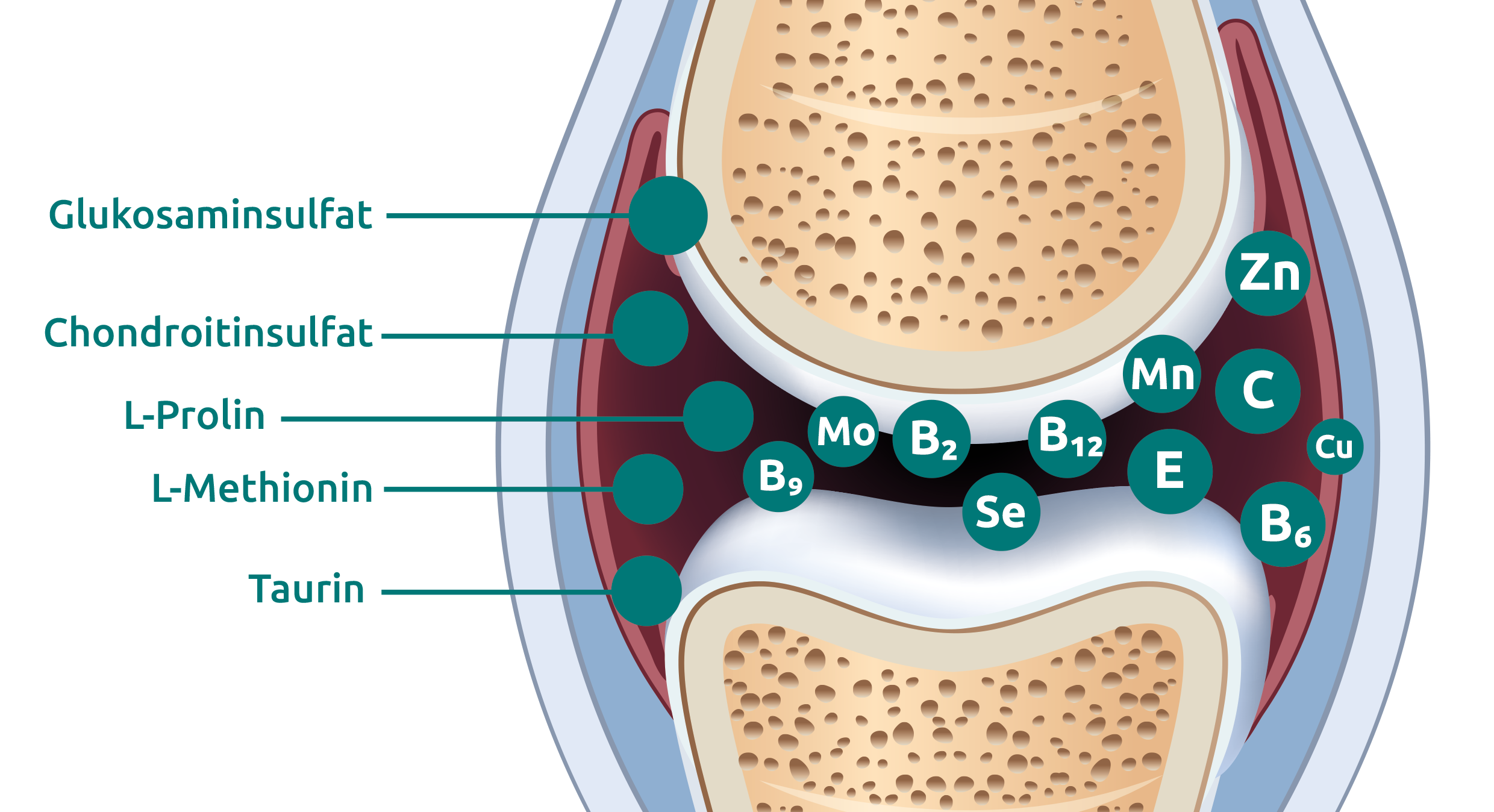
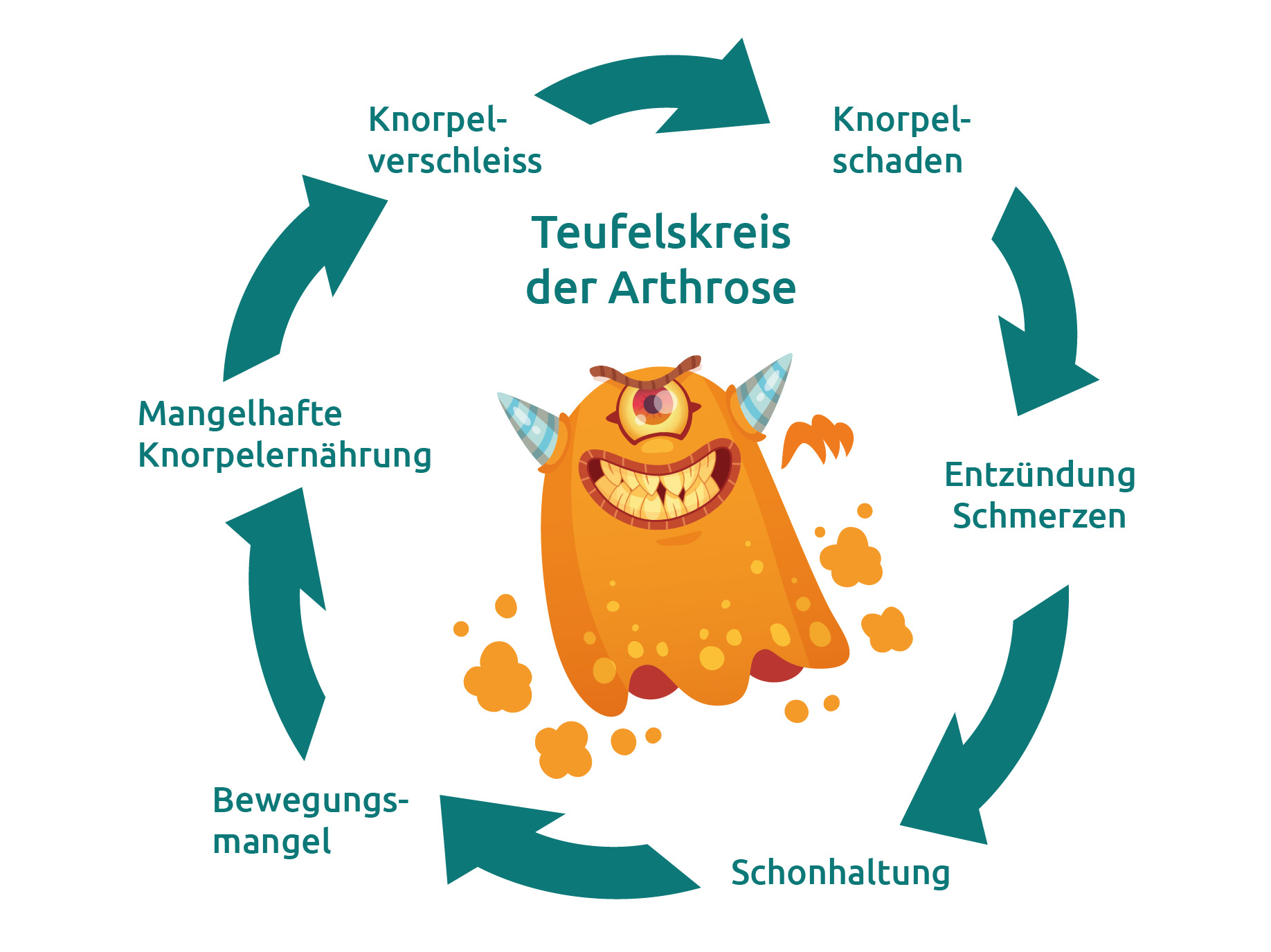
In osteoarthritis, various factors lead to progressive remodeling of the joint structures as well as frequent sclerosis and increased new bone formation in peripheral parts of the joint. This leads to a painful restriction of function, which can result in the complete loss of function of the affected joints. In osteoarthritis, all tissue layers and structures are pathologically altered. According to current knowledge, however, biochemical and molecular biological changes in the articular chondrocytes appear to be at the heart of the disease. Together with other components, these specialized cartilage cells form human cartilage tissue. It consists of only 5 % chondrocytes, which are embedded in an extracellular matrix of collagen. The proteoglycans and other structure-forming molecules contained in the matrix are responsible for the swelling pressure and elastic properties of the cartilage tissue.
However, the extracellular matrix also functions as a bioactive matrix! For example, it binds growth factors and chemokines and is able to trigger signaling cascades. If the balance is upset by damage, incorrect loading, age or biological stress, catabolic metabolic processes override the anabolic processes. This initially leads to cartilage softening, which can eventually lead to cracks and even complete loss of the cartilage layer. The destruction and detachment of cartilage components often provokes reactive synovitis. The pro-inflammatory cytokines released by the synovial membrane further intensify the degenerative process, creating a vicious circle.
-
 aminoplusMonosubstances
aminoplusMonosubstancesaminoplus® BCAA
28,90 €642,22 €/kgFood supplement with L-valine, L-isoleucine and L-leucine
Available immediately -
 aminosport®
aminosport®aminosport®
34,90 € – 89,90 €103,33 €/kg – 120,34 €/kgFood for athletes With whey protein isolate, amino acids, vitamins, minerals & trace elements
Available immediately
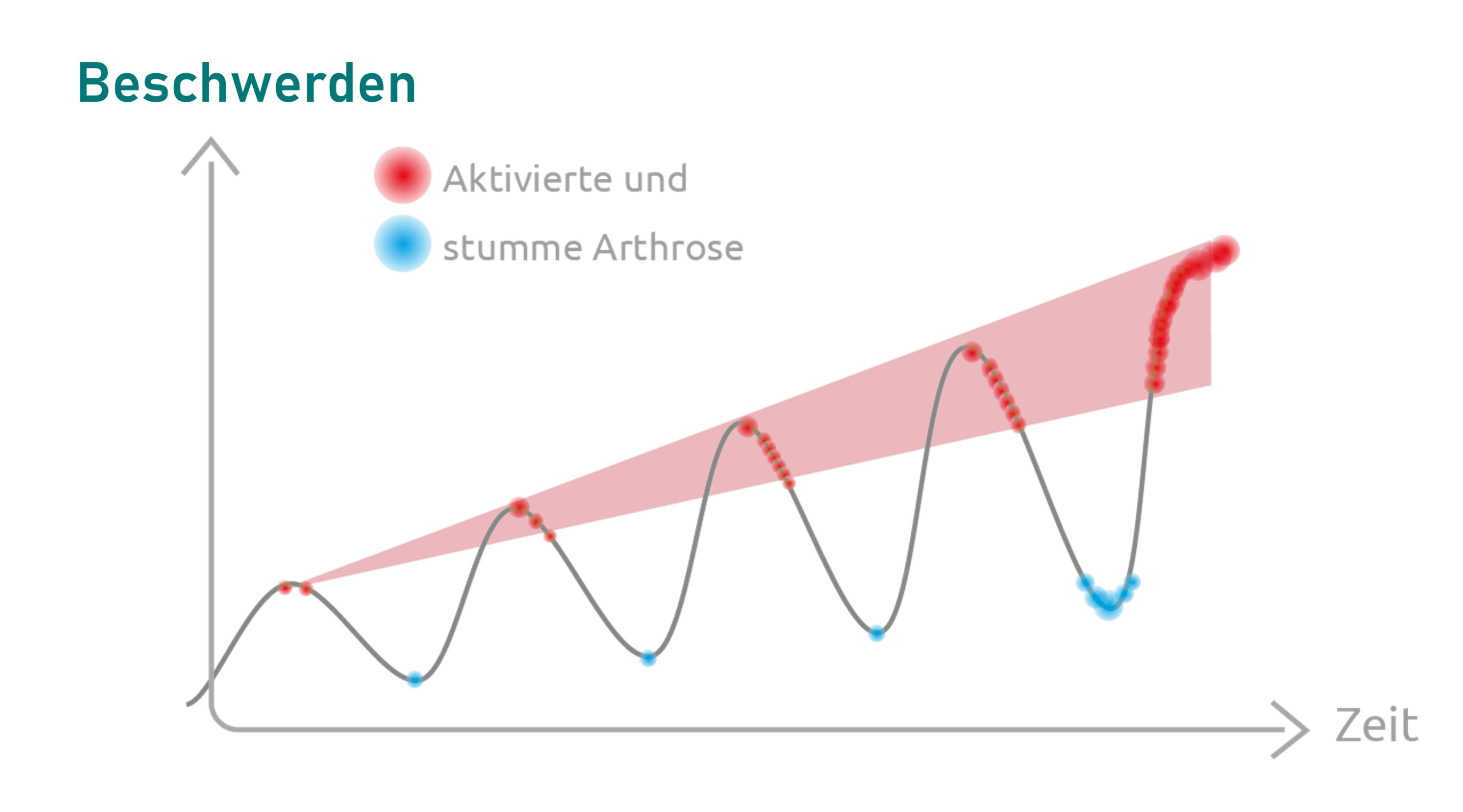
Prevention and timely intervention in therapy are therefore the be-all and end-all. In addition to avoiding overloading, overweight patients need to lose weight and exercise that is explicitly gentle on the joints, such as swimming and cycling, is desirable. “Low impact sport with incipient gonarthrosis can reduce pain, improve mobility, increase joint metabolism and strengthen the surrounding muscles and is considered an important part of conservative therapy,” the guideline states. As a first step in drug therapy, the guideline suggests the topical application of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and – if ineffective – the oral administration of ibuprofen, diclofenac and the like. However, these are associated with gastrointestinal and cardiovascular risks. Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid can also be considered for patients.
Given that the focus is on a disorder in the metabolism of the chondrocytes, the supportive use of targeted micronutrients offers a causal therapy option and thus an approach at the root. Various studies have shown that the metabolism of chondrocytes can also be positively influenced by orally ingested bioactive collagen peptides. Almost 70 percent of cartilage mass consists of collagen. Collagen consists of three polypeptide chains that are intertwined to form a triple helix. Every third amino acid in these polypeptide chains is glycine, with proline (as hydroxyproline) and hydroxylysine frequently occurring. Patented, special collagen peptides have a length of two to 20 amino acids and have been optimized and specified in such a way that they can not only be absorbed orally, but also accumulate in the chondrocytes, where they specifically stimulate the metabolism: In tissue sections, a statistically significant increase in bone metabolism could be visualized after three months of oral intake (Oesser S et al. (2007) Osteoarthritis Cartilage 15: C61.C62, 94). The intake therefore shifts the balance of catabolic, degradative processes of the chondrocytes back in the direction of anabolic processes. They thus intervene causally in the negative spiral of osteoarthritis. After just six weeks, a significant clinical improvement in the perception of pain, the feeling of stiffness and physical function was observed. The relief even improved over the course of the treatment. A prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study also demonstrated significant pain relief in 147 healthy young athletes (Penn State University, USA, 2008) with activity-dependent joint pain.
The oral administration of natural sulphur-oxygen compounds such as methylsulphonylmethane (MSM) represents a therapeutic option for intervening causally in the inflammatory process. In vitro studies indicate that MSM has an inhibitory effect on the transcription factor Nf-kB. It thus inhibits the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6 and TNF and reduces the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). Overall, the recruitment of immune cells to local inflammation is inhibited.
A study from 1995 already showed that the sulphur concentration in an osteoarthritic joint is only a third of that in Healthy cartilage. The use of MSM appears to be particularly effective in the early stages. Clinically, the use of MSM in osteoarthritis was shown by Kim et. Al(Efficacy of methylsulfonylmethane (MSM) in osteoarthritis pain of the knee: a pilot clinical trial) in 2006 in a placebo-controlled, randomized double-blind study, taking 3,000 mg twice a day actually resulted in a significant reduction in pain and improved mobility.